Whole Home Generator Maintenance Checklist
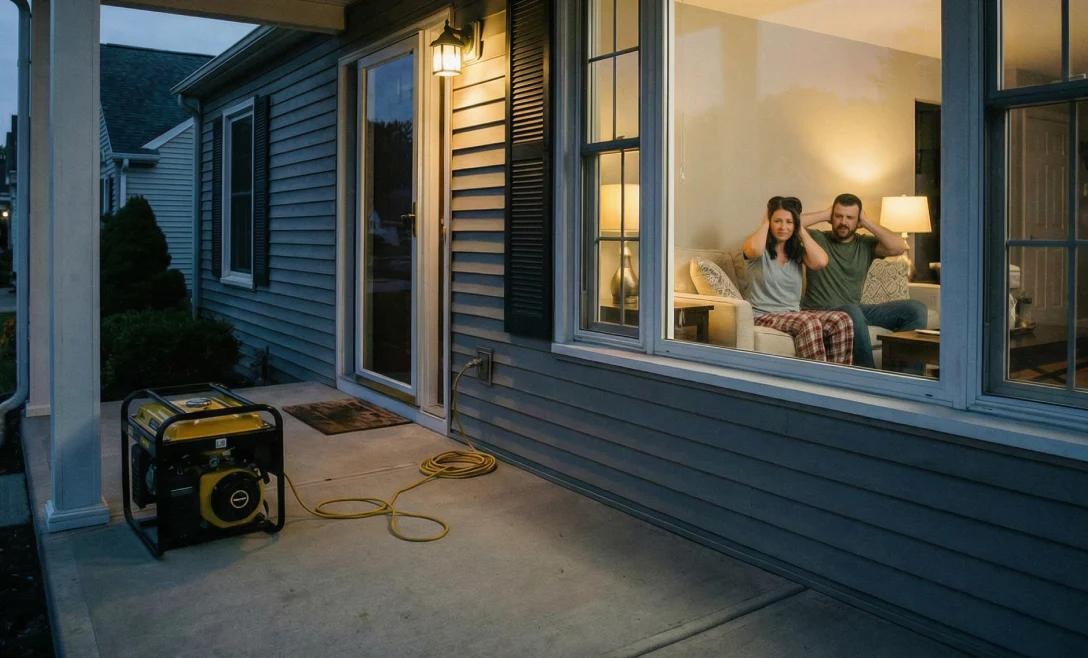
A whole home generator protects your house during power outages, but it only works well when you maintain it. Skipping normal maintenance causes rough starts, low production, and expensive repairs. A simple maintenance checklist can help homeowners stay organized and avoid breakdowns before storms come. This guide outlines the specific duties required by your generator, how frequently they should be performed, and why each step is important. Follow a simple plan to extend equipment life, protect linked appliances, and avoid emergency service calls. Regular maintenance also keeps warranties valid and guarantees that the generator produces full power when your family needs it.
What Maintenance Does a Whole Home Generator Need Regularly?
Weekly and Monthly Visual Inspections
Homeowners should do weekly and monthly visual inspections to detect issues early. Examine the generator for oil leaks, loose nuts, corrosion, and broken wiring. Check the control panel for any warning lights or error messages. Inspect hoses and belts for cracks, bulges, and fraying. Make sure the cage is level, clear of dirt, snow, and nesting animals. Confirm that the access panels are safe and locked. These rapid inspections take minutes but detect problems before they cause shutdowns. Document findings in a log so that trends emerge and service decisions are obvious. Consistent inspections promote safety and allow owners to speak openly with technicians during annual service visits.
Oil, Coolant, and Filter Checks You Must Perform
Check the oil, coolant, and filters on a regular basis, as specified by the manufacturer. Turn off the generator and allow it to cool before accessing the service panels. Use the dipstick to check the oil level and color, and then top off or change the oil as necessary. Check coolant levels and hoses to avoid overheating. Replace oil, air, and fuel filters when unclean or at the prescribed intervals. Clean components provide appropriate airflow and lubrication. These measures decrease wear, increase efficiency, and safeguard the engine under high-load circumstances. Always dispose of fluids correctly and keep track of service dates to ensure long-term compliance and dependable operation.
Battery Testing and Electrical Connection Review
Test the generator batteries to guarantee they will start reliably during outages. Inspect terminals for corrosion and clean them using the right tools. Tighten loose connections to avoid voltage dips and false warnings. Use a multimeter or built-in system to ensure the battery is fully charged. Replace aged batteries before they fail. Examine the wire, breaker, and transfer switch connections for wear or heat damage. Secure the lines and ensure the grounding is intact. Strong electrical connections keep the generator operational and your house safe from power outages. Regular testing also protects warranty terms and lowers the need for emergency troubleshooting during severe weather occurrences for households countrywide.
How to Perform Seasonal and Annual Generator Maintenance
Load Testing and Exercising the Generator
Run load tests and exercise the generator to ensure real-world performance. Start the system under controlled settings and apply electricity loads comparable to typical residential demand. Throughout the operation, keep track of the voltage, frequency, and engine reaction. Exercising the generator on a monthly or biweekly basis keeps interior parts lubricated and moisture out. Listen for odd noises and look for vibrations. After each test, shut it down and check the findings. Proper load testing ensures that the device can withstand outages and uncovers hidden issues before lengthy runtime causes damage. Schedule expert testing yearly, if necessary, and document readings to analyze performance patterns between seasons and rising home electrical needs as loads alter over time for safety.
Fuel System Inspection and Leak Prevention
Seasonal inspection of the fuel system is recommended to prevent leaks and starting issues. Check the gasoline lines for fractures, soft patches, and corrosion. Confirm that fittings are tight and free of seepage. Check for leaks in natural gas or propane systems and ensure regulators are working properly. To avoid contamination, diesel and gasoline units require fuel quality inspections. Replace old gasoline and stabilizers as necessary. Prompt fuel system maintenance decreases the risk of fire, preserves components, and guarantees that engines run consistently even during protracted outages. When servicing gasoline components, always follow local codes and manufacturer instructions to ensure safety and insurance coverage for your house and property.

Cleaning, Weather Protection, and Ventilation Checks
Clean the generator’s exterior and surrounding areas to ensure safe operation. Remove dirt, leaves, and debris that are obstructing airflow. Inspect the vents and louvers to ensure adequate ventilation and cooling. Inspect the weather seals, gaskets, and enclosure panels for damage. Confirm that the unit is still sheltered from rain, snow, and flooding. Trim any close vegetation to maintain clearance. Proper cleaning and weather protection help to reduce overheating, corrosion, and mechanical stress. Good ventilation ensures that the generator runs effectively and performs as expected over time. These tests also improve noise control and assist the system in meeting the installation spacing criteria established by local building code authorities.
Conclusion
A whole-house generator only provides value if it is properly maintained by its owners. Following a defined checklist ensures that the system is dependable, efficient, and prepared for crises. Regular inspections, fluid checks, electrical evaluations, and load testing keep minor concerns from becoming significant failures. Seasonal care to fuel, cleaning, and ventilation ensure safety and performance. Homeowners who document their upkeep and adhere to manufacturer guidelines save money on repairs. Consistent maintenance ensures that the generator starts on demand, provides reliable power, and maintains household comfort during all outages. When weather conditions become unpredictable, a well-maintained generator offers households peace of mind and reliable backup power.
Disclaimer
This article is intended for general informational purposes only and does not replace the manufacturer’s instructions, professional advice, or local electrical and safety codes. Generator models, fuel types, and installation requirements vary, and maintenance procedures may differ depending on the manufacturer and system design. Always consult your generator’s owner’s manual and follow the manufacturer’s recommended service intervals and safety guidelines. Certain maintenance tasks should only be performed by licensed or qualified technicians to reduce the risk of injury, equipment damage, fire hazards, or voided warranties. The author and publisher assume no responsibility for damage, loss, or injury resulting from the use or misuse of the information provided in this article.